The calculation methods for normal revenue and financial profit differ of their remedy of revenue and expenses, resulting in distinct perspectives on a business’s financial efficiency and profitability. Understanding these variations is important for assessing the general economic success of a company. Within a company, regular revenue influences the evaluation of the worth of manufacturing, market structure dynamics, and the company’s long-run equilibrium. It serves as a important measure for evaluating the sustainable profitability of the company in a aggressive market environment. In competitive equilibrium, market situations play a pivotal position in shaping the interpretation of regular revenue.
By the end of this article, readers will achieve a thorough understanding of normal profit, equipping them with the data to make informed financial assessments and strategic enterprise decisions. Regular profit is greater than only a theoretical benchmark—it is a vital idea that determines whether or not a enterprise is economically sustainable. It acts as a threshold that reflects the opportunity price of entrepreneurial sources.
It allows for the excellence between accounting profit and economic revenue, providing insights into the traditional profitability of a enterprise inside its trade. Numerous components can affect the level of regular revenue attained by a enterprise, including competitors dynamics, adjustments in demand patterns, economic situations, and the management of business expenses. Understanding these factors is essential for assessing a company’s financial performance and sustainability. Recognizing the impact of those concepts is essential for knowledgeable decision-making. Normal revenue is claimed to happen when the corporate earns revenue equal to the implicit and express value of the corporate. The scenario in macroeconomics occurs when the trade experiences perfect competitors.

Definition Supernormal Revenue
Nevertheless, economists additionally assume that companies might goal to maximize revenue (profit is income – cost), maximize market share or obtain a pre-defined level of revenue. Accounting revenue occurs when revenues are higher than prices, and never equal, as in the case of regular profit. Regular revenue is calculated by subtracting the whole prices of a enterprise from its whole income. The resulting amount represents the minimal revenue required for a business to break even and cover its costs. The timeframe thought of for normal profit and economic profit assessments considerably influences the evaluation of long-run market equilibrium and the efficient allocation of assets within a business.

The Uk Financial System: Efficiency & Policies
The concept primarily applies when analyzing capitalist wealth extraction strategies. Specific prices are direct, out-of-pocket payments for expenses like wages, hire, and supplies that companies incur during manufacturing. For instance, in the case of the tech business, corporations like Apple and Microsoft have demonstrated the worth of long-term planning, permitting them to innovate and preserve market management. By considering temporal dimensions in profit assessments, businesses can better place themselves for long-term success. Normal revenue also shapes the long-term sustainability of the company by influencing useful resource allocation, market positioning, and the ability to face up to competitive pressures.
- Regular profit is calculated by subtracting total bills, together with each explicit and implicit costs, from complete income.
- Marginal value is the additional cost incurred from producing one more unit of an excellent or service.
- Regular profit happens when economic revenue is zero, or when the total revenue of an organization equals the sum of implicit value and specific value.
- Normal profit exerts a direct affect on a company’s financial statements, particularly in figuring out the traditional rate of return on invested capital and assessing the overall financial well being of the business.
- Regular revenue, in the context of accounting and economics, refers back to the stage of profit that permits a company to cover all of its costs together with explicit and implicit costs, thereby reaching a state of market equilibrium.
Normal revenue in accounting refers again to the quantity of revenue that a company earns which is just sufficient to cover its prices and supply a fair return to its owners or investors. It is also referred to as the minimal level of revenue necessary for a enterprise to proceed working. To navigate these challenges, strategic considerations corresponding to pricing methods, cost controls, and diversification are crucial for companies to sustain normal profit ranges.
It makes the business highly aggressive and can attain a stage of normal revenue. In the tech industry, reaching normal revenue may be particularly challenging due to high implicit prices similar to foregone salaries for skilled personnel and delayed returns on early investments. Tech startups typically run at a loss initially whereas striving to succeed in the traditional revenue benchmark as they scale. Traders often have a look at a company’s capacity to supply income past normal profit when making funding decisions. Constructive financial revenue indicates that the company is a worthwhile investment as it means the corporate is using resources effectively.
Regular revenue happens when a company’s total revenue equals its whole prices, each explicit and implicit. Regular profit is the minimal stage of revenue that a firm should earn in the long run to remain in business. Regular profit is considered a price as a outcome of it represents the chance cost of utilizing assets in a selected business as an alternative of pursuing various opportunities. It includes https://www.simple-accounting.org/ both express costs (actual expenses) and implicit prices (opportunity costs) and is important for a business to proceed operating in the lengthy term.
Regular revenue is the minimal level of profit a firm should earn to remain in enterprise in the long term. It represents the opportunity value of the agency’s sources, or the returns the agency’s owners may earn by employing their sources elsewhere in the financial system. Accounting revenue is the excess generated when a business’s complete income exceeds its explicit costs inside a specific interval, similar to a financial 12 months.
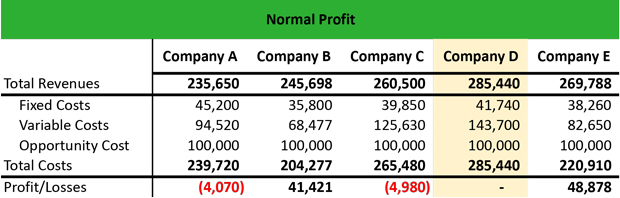
Specific costs are direct expenses like employee salaries, raw material costs, and lease. Of the 5 firms, firm A and company C incur losses of $4,070 million and $4,980 million, respectively. Company B and company E notice a achieve of $41,421 million and $48,878 million, respectively. Firm D has a NP as a outcome of the difference of the total revenues minus the entire prices is zero. The distinction between a firm’s whole revenue and its specific prices, not including implicit costs.

